How Much Tax Money Is There Per Year In Sa
A breakdown of the taxation pie
Note: The original version of this article was published on 25 June 2019, with the international revenue enhancement-to-Gross domestic product ratio figures based on information from the IMF. After discussions with National Treasury, it was agreed that tax-to-Gdp figures from the OECD provide a more relevant movie when Due south Africa is compared with other countries, every bit the International monetary fund data practise not include social security contributions or provincial taxes. The article was revised on 12 July 2019 to reflect this.
Personal income tax has become more important as a source of government revenue in contempo years. Stats SA's latest publication provides a breakdown of the latest tax data from national government.
Personal income tax contributed over a third of the R1,22 trillion in taxes collected by national regime in the 2017/18 fiscal year, according to Stats SA'south Fiscal statistics of national authorities report. The 2d biggest source of taxation was value added tax (VAT), followed by company income tax (click on the image to enlarge).
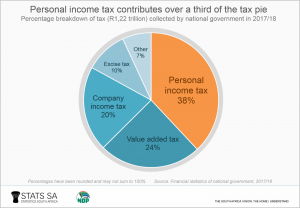
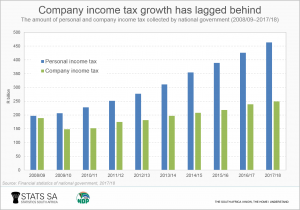
The tax mix looked starkly different a decade ago. In 2008/09, national government collected well-nigh the same amount of personal income and company income taxation: contributions that year were 31% and 30% respectively.
The 2008–2009 global financial crisis, which resulted in South Africa'south first economic recession since 1994, was specially hard on businesses. Revenue from company income tax declined in 2009/ten, and since and then has grown at a much slower rate than the corporeality collected from personal income tax.
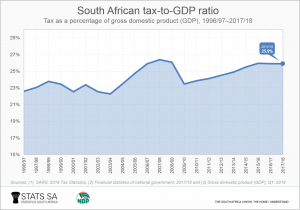
Tax acquirement has been increasing despite weak economic growth. The taxation-to-Gdp ratio, which gives a sense of the taxation burden, shows tax revenue as a percentage of gross domestic product (Gross domestic product). In 2017/18, Southward Africa's tax-to-GDP ratio was 25,ix%.1 The chart below shows how the taxation-to-GDP ratio has grown since the tardily nineties, peaking at 26,iv% in 2007/08.2 The higher the percentage, the higher the amount of taxation collected relative to the size of the economy.
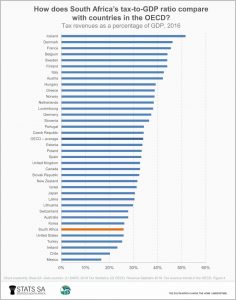
How does Due south Africa compare with other countries in terms of the tax-to-GDP ratio? Information are available from both the International Budgetary Fund (IMF) and the Organisation for Economical Co-operation and Development (OECD). The International monetary fund places Southward Africa in the tiptop 10 list of countries with the highest tax-to-Gdp ratio.iii
However, it is important to annotation that the International monetary fund data exclude social security contributions and provincial/state taxes. The OECD data, on the other hand, practise include these 2 items. Since some countries rely more heavily on social security contributions and regional taxes than South Africa, the OECD data provide a more relevant moving-picture show for making comparisons.
Compared with the 36 member countries of the OECD, South Africa finds itself at the lower end of the chart beneath, with a smaller tax-to-Gdp ratio than the Great britain, Greece and Italy.4
Is having a high tax-to-Gdp ratio a good or a bad affair? Information technology depends on each country. For a nation that has a high ratio but where taxpayers are receiving adept value for money, a high tax burden might not be that detrimental. Countries such as Denmark, Sweden and Finland have high tax-to-GDP ratios, only these nations report the highest standard of living.
A very low tax-to-GDP ratio can be problematic equally it may be a sign of an inefficient revenue enhancement system. A government will struggle to provide services, build infrastructure or maintain public goods if it fails to collect taxes during periods of strong economic growth. Indonesia, for example, has in recent years committed itself to raise its tax-to-Gross domestic product ratio from 10% to xv%.5
The tax-to-Gdp ratio alone provides no indication of good governance, the efficiency of the taxation organisation in the state, nor the fashion in which taxes are used or distributed.
For more data, download the latest Financial statistics of national regime release and accompanying Excel data here.
1 That'southward tax collected (R1,22 trillion) divided by the GDP in current prices (R4,69 trillion).
ii The taxation data prior to 2005/06 in the chart are courtesy of SARS and National Treasury. Source: South African Revenue Service (SARS) and National Treasury, 2018 Tax Statistics, Tabular array ane.6 (run into here). The chart has been updated with revised GDP figures from Stats SA.
three International Budgetary Fund (IMF), Government Finance Statistics Yearbook and information files. The data are available from the Globe Bank information portal (access the data here).
4 OECD, Revenue Statistics 2018, Tax revenue trends in the OECD, Table one (read here)
5 The Jakarta Mail service, Republic of indonesia'south low tax-to-Gdp ratio (read here).
Like manufactures are bachelor on the Stats SA website and tin can exist accessed here.
For a monthly overview of economic indicators and infographics, catch the latest edition of the Stats Biz newsletter hither.
Source: http://www.statssa.gov.za/?p=12238
Posted by: davisthaverom67.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Much Tax Money Is There Per Year In Sa"
Post a Comment